Temporal Bone and Skull Base Trauma
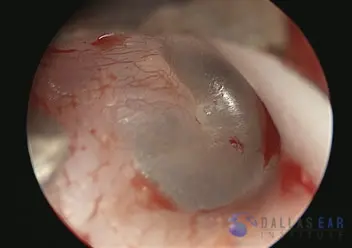
Temporal Bone and Skull Base Trauma
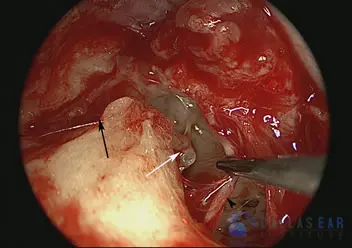
The ear drum has been elevated surgically. The bony defect is shown with the black arrow. There is a large gap in the bone of the ear canal. The white arrow points towards the hearing bones in the middle ear.
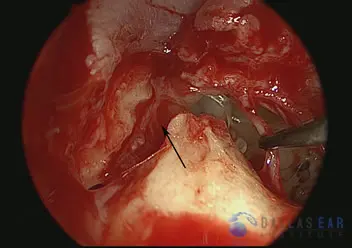
The fracture and resultant gap in the ear canal bone is shown with the black arrow. The chorda tympani taste nerve is gently retracted with the suction.
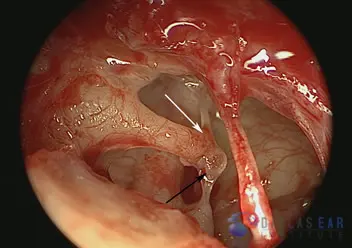
The hearing bones are clearly seen to be disarticulated, or separated. The white arrow is pointing towards the incus, the 2nd hearing bone. The black arrow is indicating the stapes, the 3rd hearing bone. The trauma has caused the incus to separate from where it attached to the stapes. Thus, there is no connection among the hearing bones for conduction of sound into the inner ear.

The incus bone has been removed from the middle ear because it is no longer attached to the stapes. In it’s place, a prosthetic bone is placed. This particular prosthesis is made of hydroxyapatite and titanium, and is used to bridge the gap between the first and third hearing bones so that sound may be conducted into the inner ear. Many different prostheses may be used for hearing reconstruction.
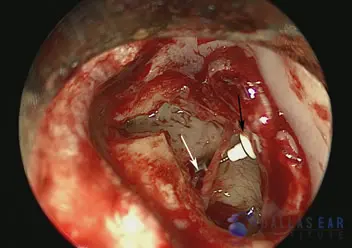
The prostheses has been inserted under the malleus first hearing bone (black arrow) and on to the stapes third hearing bone (white arrow).
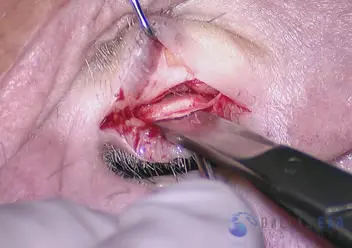
Cartilage and perichondrium (the tissue attached to the cartilage) are utilized to repair the large defect in the ear canal caused by the trauma. The cartilage is harvested from the ear and trimmed for use.
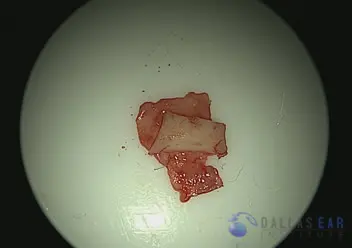
Cartilage and perichondrium graft after preparation.
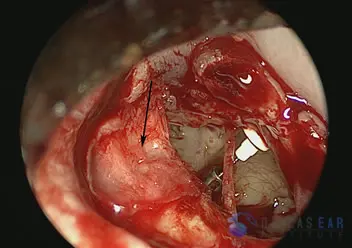
The cartilage is used to reconstruct the gap in the bone and the attached perichondrium is draped over the ear canal to maintain the positioning of the cartilage graft. This prevents the ear canal skin from retracting into this defect and trapping within the defect.
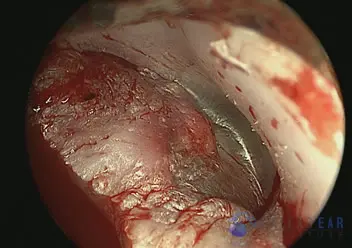
The ear drum is replaced onto the reconstruction.

